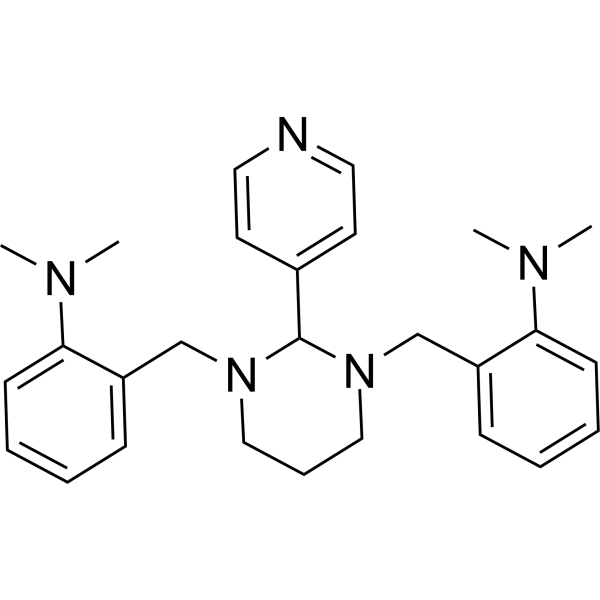
Chemical, computational and functional insights into the chemical stability of the Hedgehog pathway inhibitor GANT61
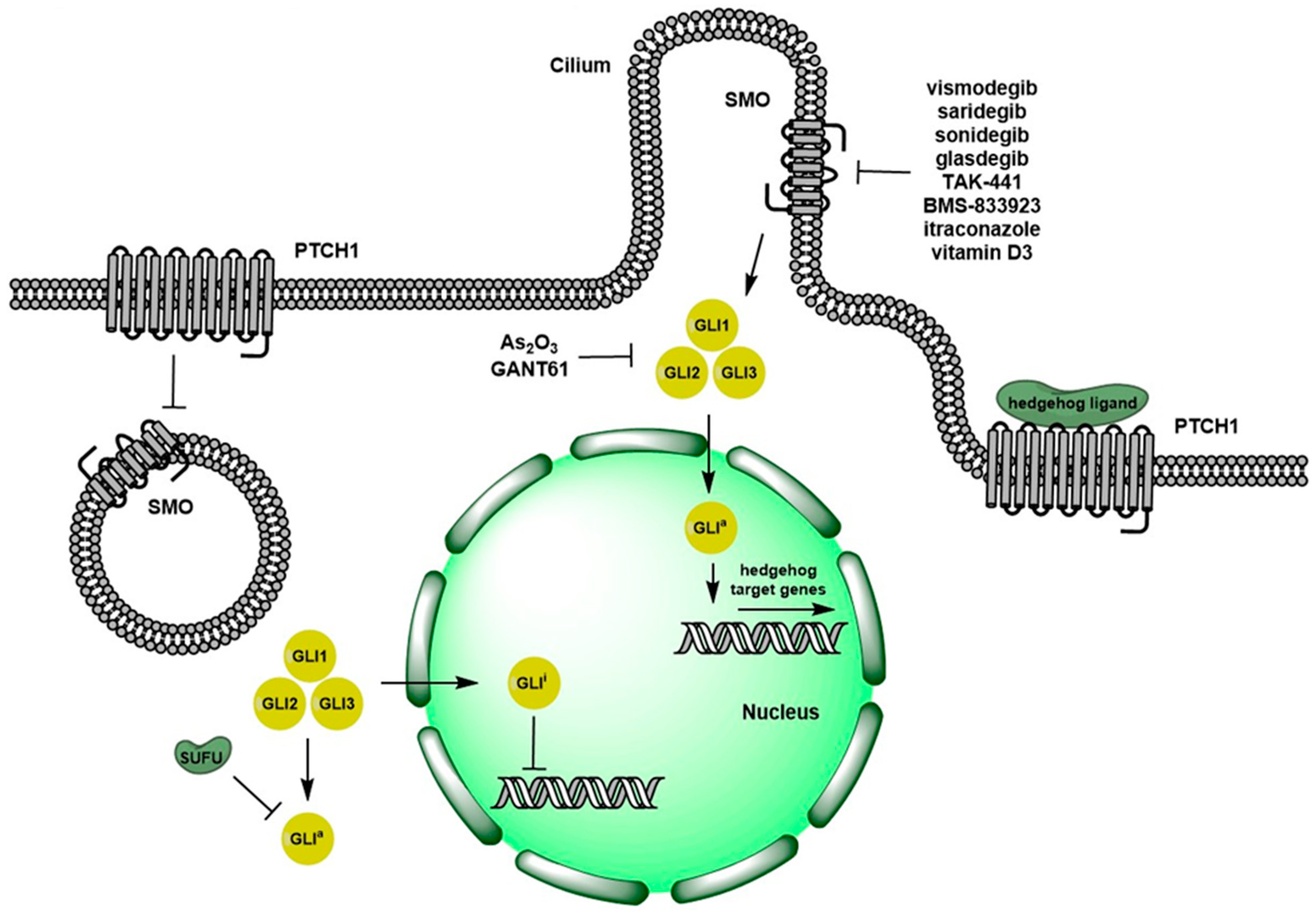
Cells | Free Full-Text | Recent Advances in the Clinical Targeting of Hedgehog/GLI Signaling in Cancer | HTML
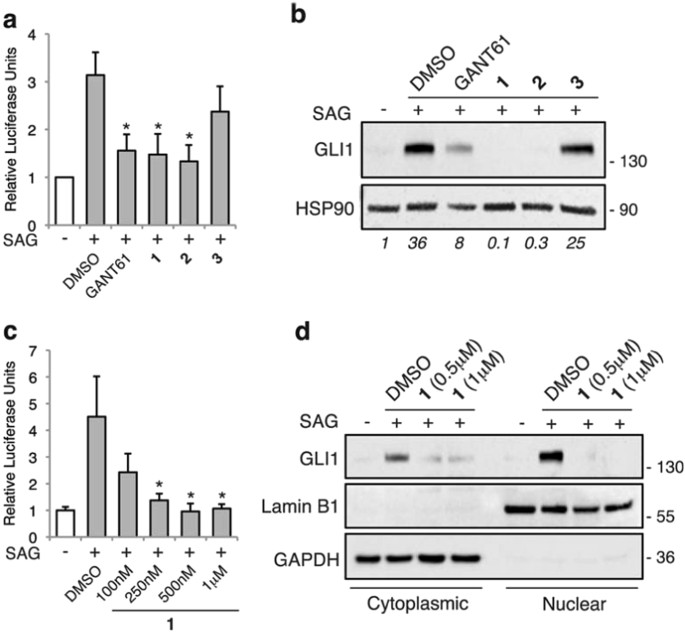
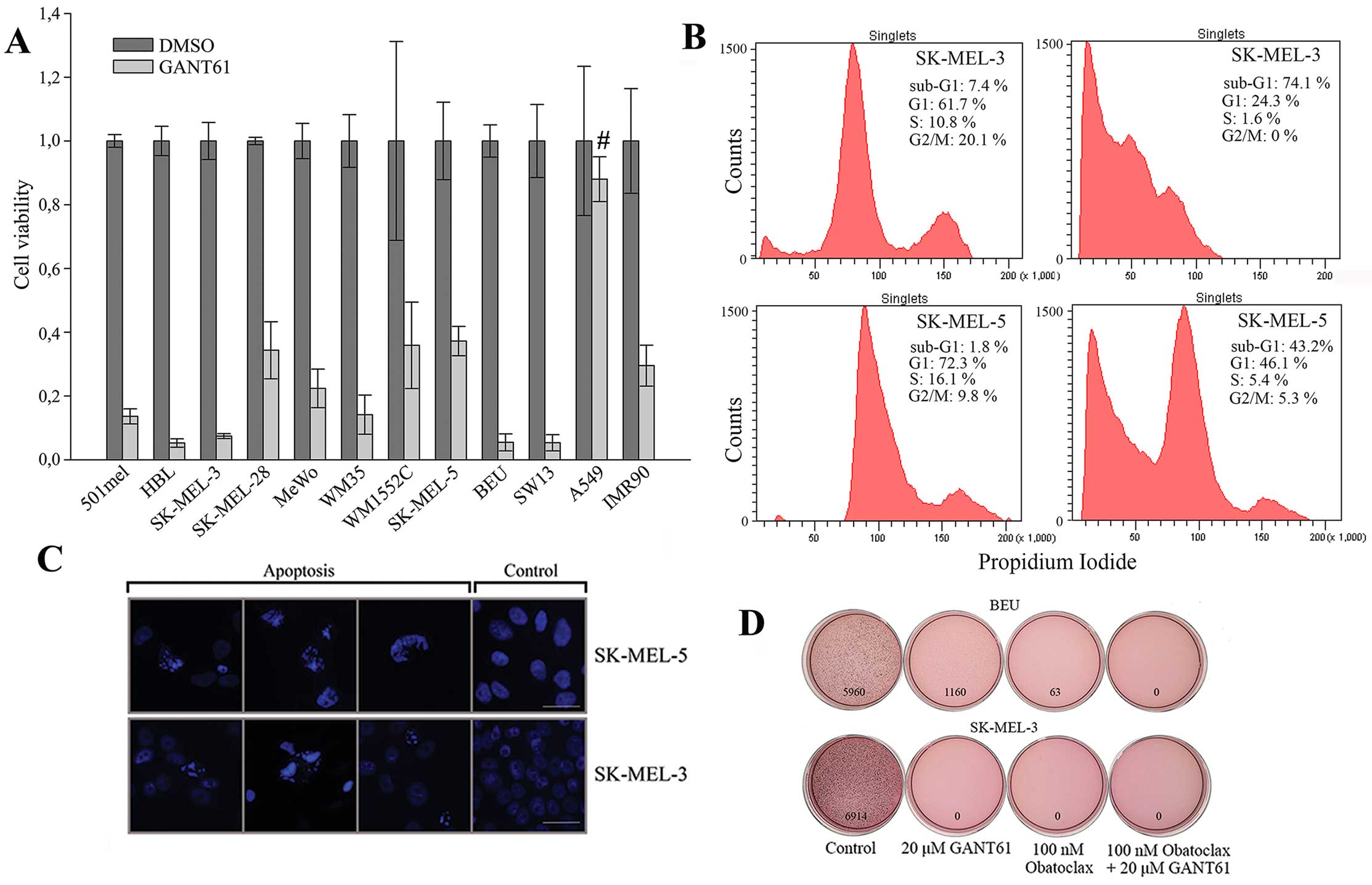
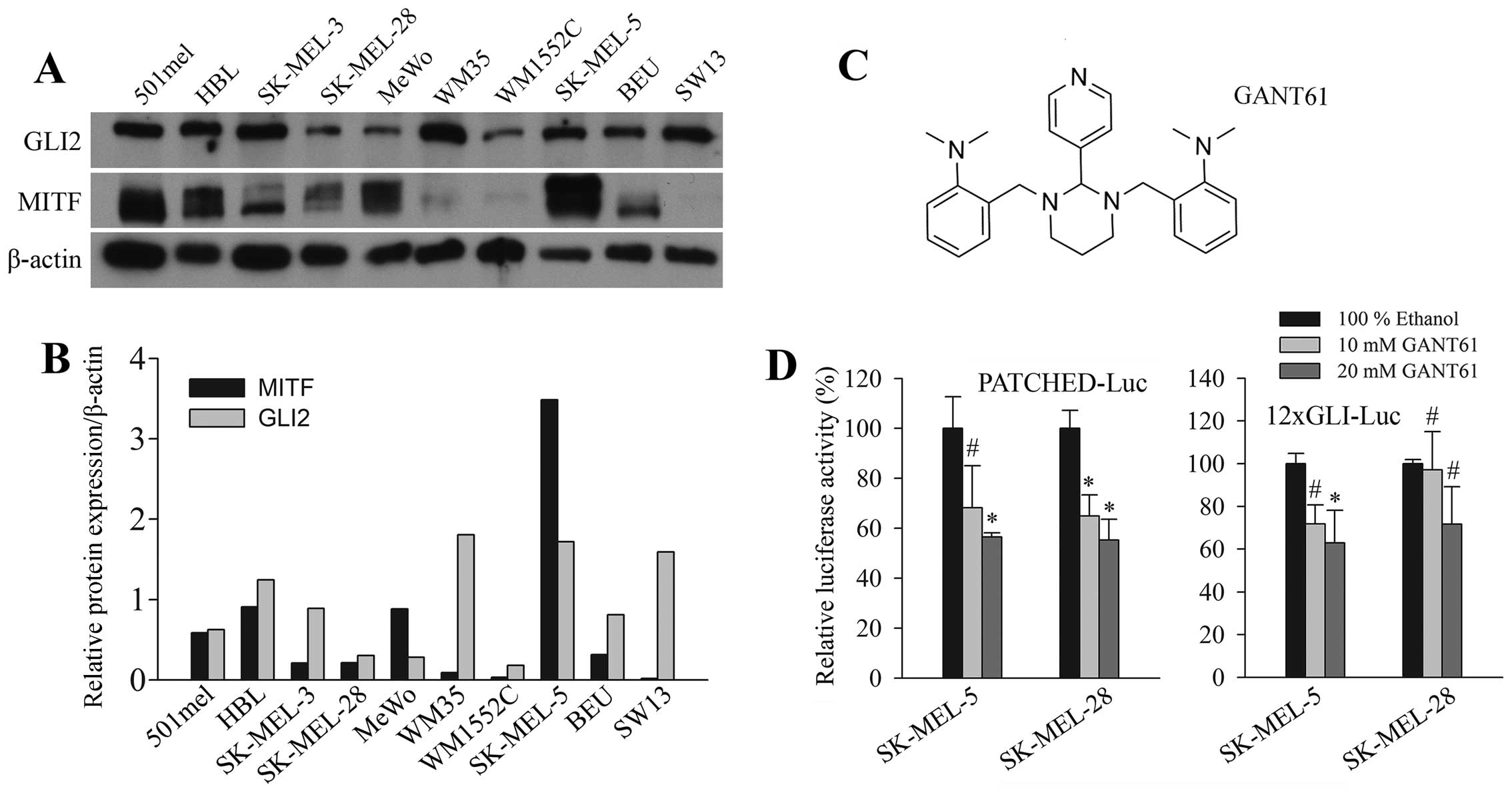
Targeted inhibition of Hedgehog-GLI signaling by novel acylguanidine derivatives inhibits melanoma cell growth by inducing replication stress and mitotic catastrophe | Cell Death & Disease

Targeting the hedgehog signal transduction pathway at the level of GLI inhibits neuroblastoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo - Wickström - 2013 - International Journal of Cancer - Wiley Online Library
Chemical, computational and functional insights into the chemical stability of the Hedgehog pathway inhibitor GANT61

GANT-61 treatment to RMS cells inhibits proliferation, colony formation... | Download Scientific Diagram
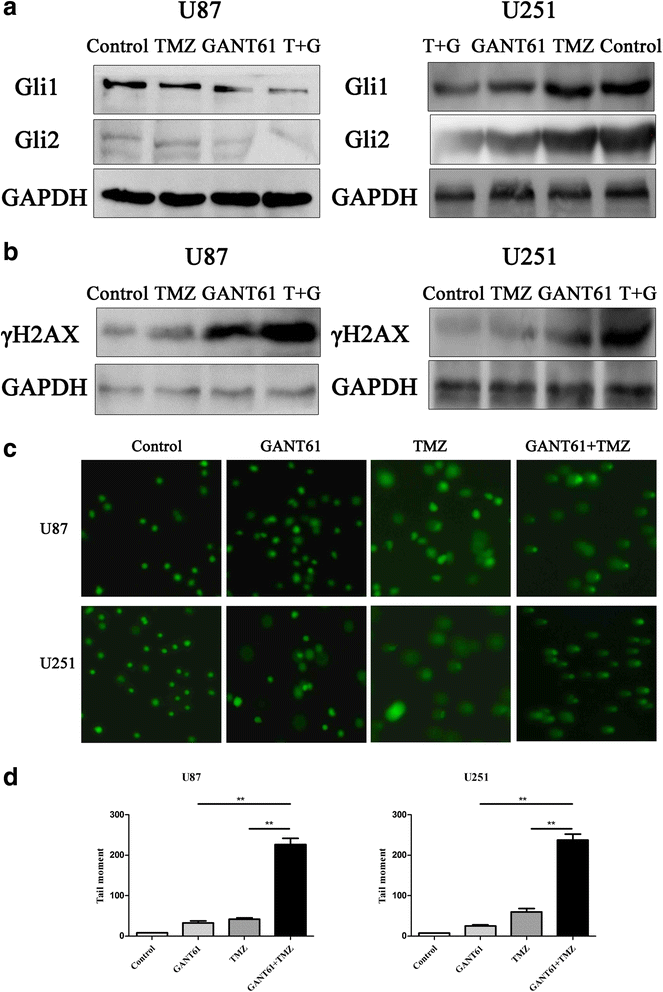
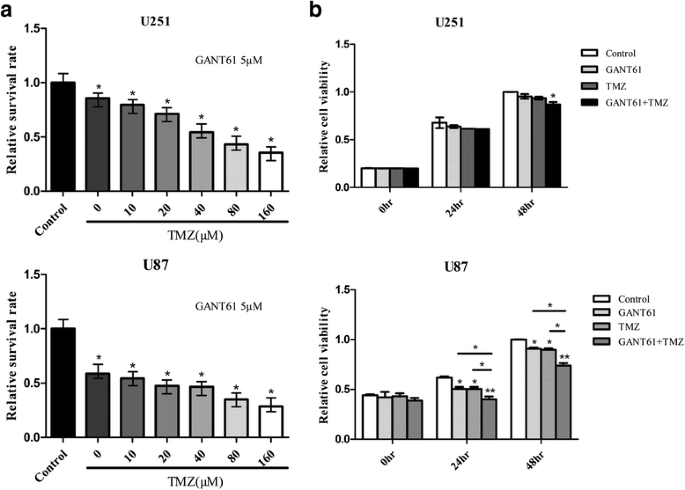
GANT61, a GLI inhibitor, sensitizes glioma cells to the temozolomide treatment | Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research | Full Text

Reproducibility of academic preclinical translational research: lessons from the development of Hedgehog pathway inhibitors to treat cancer | Open Biology

Targeting the hedgehog signal transduction pathway at the level of GLI inhibits neuroblastoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo - Wickström - 2013 - International Journal of Cancer - Wiley Online Library

The role of hedgehog signaling in gastric cancer: molecular mechanisms, clinical potential, and perspective. - Abstract - Europe PMC
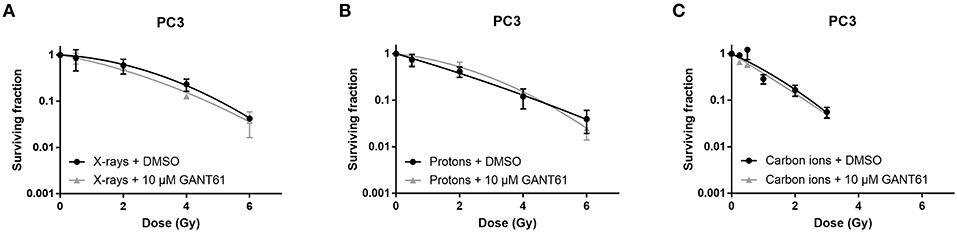
Frontiers | The Combination of Particle Irradiation With the Hedgehog Inhibitor GANT61 Differently Modulates the Radiosensitivity and Migration of Cancer Cells Compared to X-Ray Irradiation | Oncology
Chemical, computational and functional insights into the chemical stability of the Hedgehog pathway inhibitor GANT61

Effect of GANT61 and IR in vivo. (A) Relative tumor growth of 22Rv1... | Download Scientific Diagram